Using Resource Scripts
Resource scripts allow you to add automation to specific sandbox components. These scripts are intended to add simple functionality, or to be used for testing and debugging activities. Note that in order to add automation to a shell, the best practice is to use the component’s driver.
Using the script_helper
Resource scripts get information from the sandbox component using the script_helper.
To use the script helper:
Import the cloudshell-automation-api python package and add it to your script, as illustrated in the example below. Note that the package is automatically imported when your sandbox starts. In this example, the following code gets an object that contains all of the sandbox’s information:
import cloudshell.helpers.scripts.cloudshell_scripts_helpers as script_helpNote that to execute this code, you will need to include a requirements.txt file in your script.
To facilitate writing and debugging activities, it is recommended to use advanced IDEs such as PyCharm, which provide autocomplete functionality, as illustrated below.
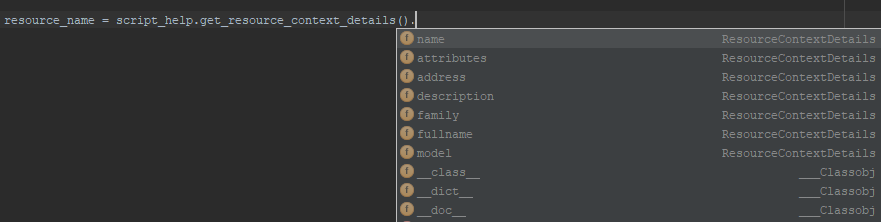
Accessing the sandbox component
Use the get_resource_context method to access and use the sandbox component in your resource script.
For example, let’s assume we want to get metadata information from the component, such as name and address:
resource_name = script_help.get_resource_context_details().name
resource_address = script_help.get_resource_context_details().addressOr to get information from attributes on the component:
- For global attributes, use the attributes element. For example, “Region” and “Execution Server Selector”:
resource_region = script_help.get_resource_context_details().attributes.Region
resource_ess = script_help.get_resource_context_details().attributes["Execution Server Selector"]- For namespaced attributes (i.e. attributes that exist on a 2nd Gen shell only), provide the full attribute name, including the namespace. For example, “Vendor” and “OS Version”:
resource_vendor = script_help.get_resource_context_details().attributes['CS_Switch.Vendor']
resource_os_version = script_help.get_resource_context_details().attributes['CS_Switch.OS Version']Using API from the resource script
To use the API, create a session variable that uses the helper’s get_api_session method:
session = script_help.get_api_session()Associating a resource script to a CloudShell resource
1) Place the python script(s) and requirements.txt files in a folder.
2) From within the folder, select the two files and zip.
3) In CloudShell Portal’s Scripts management page, open the Resource Scripts page and add the zip file.
4) Edit the script and from the Models drop-down list, select the models of the resources and services.
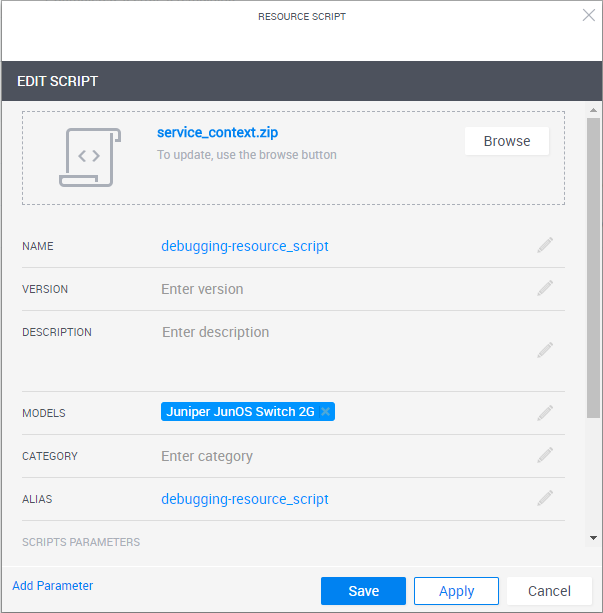
5) Click Save.
Example
In this example, we use the CloudShell Automation API to get the resource’s vendor and OS version:
requirements.txt
cloudshell-automation-api>=8.1,<8.2__main__.py
import cloudshell.helpers.scripts.cloudshell_scripts_helpers as script_help
session = script_help.get_api_session()
resource_vendor = script_help.get_resource_context_details().attributes['CS_Switch.Vendor']
resource_os_version = script_help.get_resource_context_details().attributes['CS_Switch.OS Version']
session.WriteMessageToReservationOutput(
reservationId=script_help.get_reservation_context_details().id,
message='the resource vendor is {}'.format(resource_vendor)
)
session.WriteMessageToReservationOutput(
reservationId=script_help.get_reservation_context_details().id,
message='the resource OS version is {}'.format(resource_os_version)
) CloudShell Developer Guide
CloudShell Developer Guide